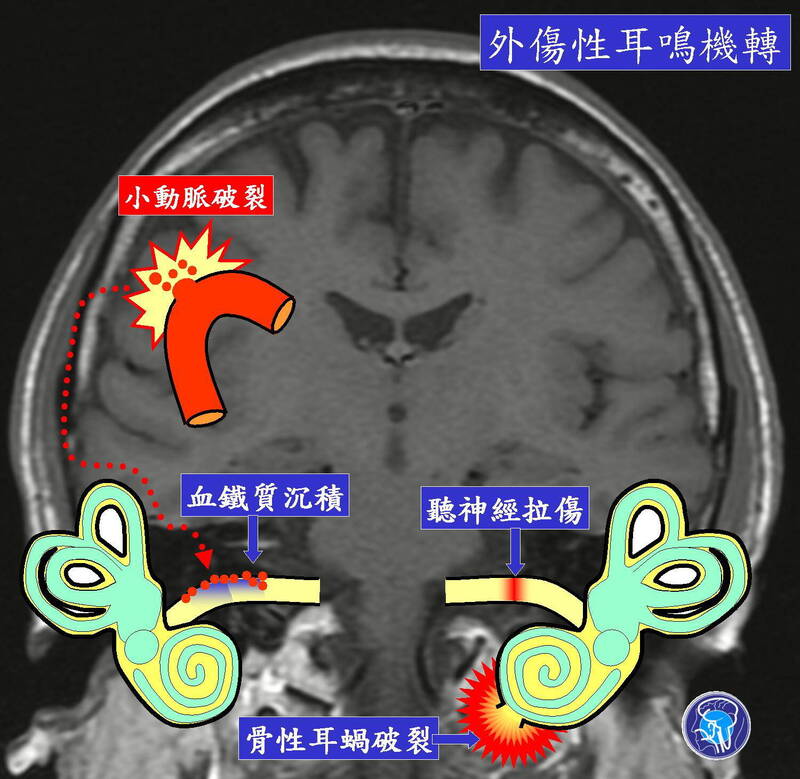
The mechanisms of traumatic tinnitus include auditory nerve strain, bony cochlear rupture, and hemosiderosis.
(Provided by Chen Jianzhi and Zeng Bingtao)
[Health Channel/Comprehensive Report] Head injuries caused by accidents may also cause tinnitus.
Physicians Chen Jianzhi and Zeng Bingtao of Yuanjing Otorhinolaryngology Neurology Clinic said that head trauma may lead to temporal bone hematoma, auditory ossicle chain rupture, cochlear artery syndrome, cervical spine trauma, auditory nerve strain, bony cochlear rupture, and hemosiderosis, which in turn lead to Tinnitus of different nature.
Chen Jianzhi and Zeng Bingtao pointed out that due to a certain head trauma, such as a car accident, fall, fight, ball game or industrial safety accident, some patients had already started to feel full in one ear before being sent to the hospital, and heard a chaotic "crack" sound, or High-frequency "humming" sound, but the tinnitus disappeared after seeking medical treatment, but there are still some people who gradually develop tinnitus after recovery, and it gets worse year by year.
Please read on...
Chen Jianzhi and Zeng Bingtao pointed out that there are seven common reasons for this phenomenon:
Temporal bone hematoma:
due to head impact, the bone trabeculae in the temporal bone gas room are brittle, and the mucosa is torn and bleeding gradually overflows to the middle ear cavity, blocking the vibration of the auditory ossicles or eardrum when sound transmission occurs, resulting in conductive hearing loss, leading to compensation Sexual tinnitus.
●Breakage of the auditory ossicle chain:
the impact wave passes through the middle ear cavity, the auditory ossicles are fractured or the joints are dislocated, unable to conduct sound waves, conductive hearing loss occurs, and compensatory tinnitus occurs.
●Cochlear artery syndrome:
temporal bone trauma, mucosal tearing cause bacterial invasion, local inflammation, a large number of macrophages, white blood cells and antibodies stray into the narrowed cochlear artery blockage.
If it occurs in the front cochlear artery, it will cause high-frequency tinnitus; if it occurs in the rear cochlear artery, it will cause low-frequency tinnitus.
Cervical spine trauma:
Cervical intervertebral disc protrusion or vertebral body deformation compresses the spinal nerve foramen and the spinal nerves inside, a large amount of sensory information is transmitted to the rear spinal cord, and is transmitted upward to the brainstem. , Interfering with the auditory nerve pathway of the lateral hoof system, affecting the transmission of auditory information, resulting in brainstem tinnitus, also known as "brain tinnitus".
●Auditory nerve strain:
The fracture line of the temporal bone passes through the internal auditory canal, and the auditory nerve is pulled and injured. The auditory signal generated by the inner ear cannot be transmitted to the brainstem, resulting in neurological hearing impairment and compensatory tinnitus.
●Bone cochlear rupture:
the bony shell of the cochlea of the inner ear is ruptured, the perilymph fluid leaks, and shear force displacement occurs between the hairs on the organ of Cordon and the tectum, which produces auditory signals and cochlear tinnitus.
Hemosiderosis:
rupture of small pia mater arteries, red blood cells enter the cerebrospinal fluid circulation, attach to the auditory nerve, and then dissolve to produce hemeogen, decompose into iron free radicals, poison nerve myelin sheath and axons, and appear inflammatory Tinnitus, causing nervous hearing impairment.
Head trauma causes temporal bone hematoma, bacteria invade mucosa, and local inflammation causes cochlear artery syndrome.
(Provided by Chen Jianzhi and Zeng Bingtao)
Chen Jianzhi and Zeng Bingtao said that tinnitus that occurs after head trauma is called traumatic tinnitus. Hearing examination, middle ear analysis, computer tomography or MRI will be arranged, and treatment will be given according to the cause:
●For temporal bone hematoma, auditory nerve damage (strain) or bony cochlear rupture, bed rest is recommended for natural recovery.
●If the auditory ossicle chain is broken or the cervical spine is fractured, surgical repair or correction is recommended.
●For cochlear artery syndrome, it is recommended to inject high-dose antibiotics intravenously to directly kill bacteria and reduce inflammation.
●For hemosiderosis, the bleeding site should be found first, and the bleeding should be directly operated to stop the bleeding. Otherwise, a fat-soluble iron chelator (deferipone) can only be taken orally to remove iron deposits through the blood-brain barrier and prevent neurotoxicity.
☆Health news will never be missed, click like to follow the fan page.
☆For more important medical news, please go to Liberty Health.com.
keywords
tinnitus
dizzy
head trauma
Cerebral tinnitus
related news