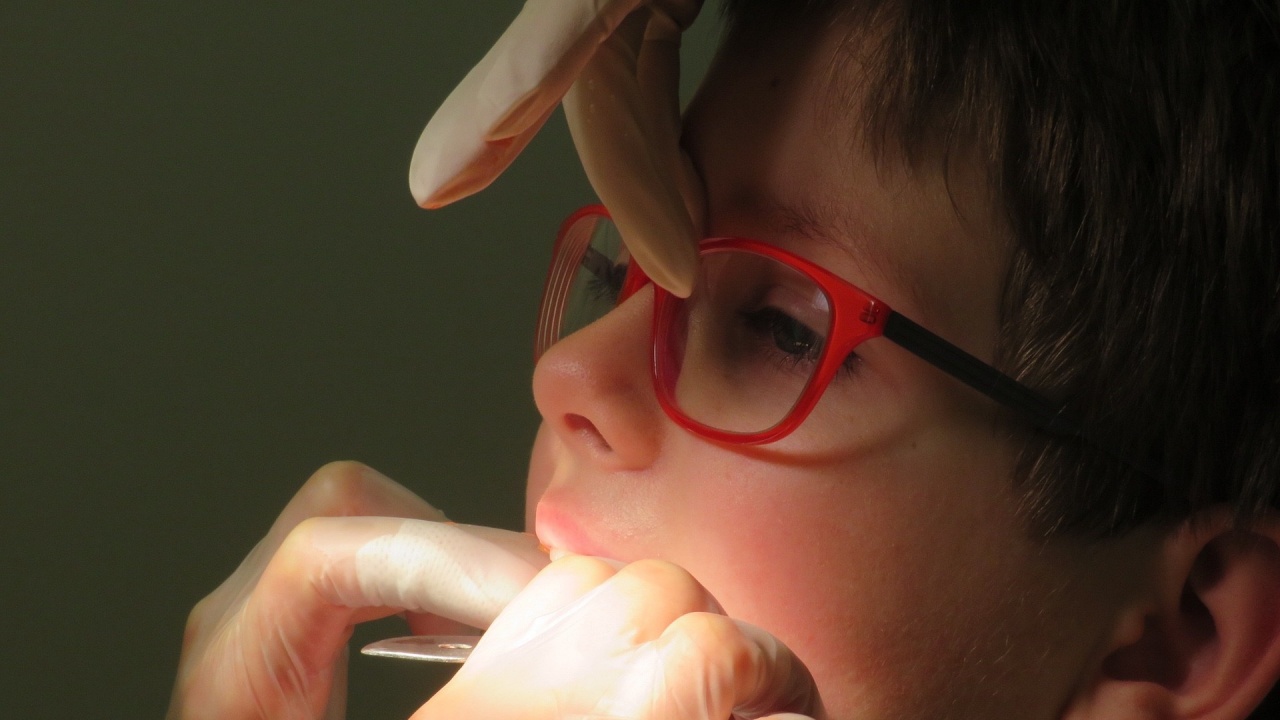
For ten years, 160,000 children have been covered by the dental silanization program. This was told to journalists by Dr. Nikolay Sharkov, chairman of the Bulgarian Dental Union (BZS). Placing sealants on the first permanent molars of children aged 5-9 in Bulgaria began in 2011. The purpose of silanization is to preserve the surface of the teeth, BTA reported.
The prevention of oral diseases should be the concern of the state, Dr. Sharkov added.
People ignore some oral diseases, but there is a proven link between oral diseases and general diseases.
Caries and their complications, periodontitis, dental trauma, dental erosion, precancers and cancer of the oral cavity are associated with the risk of cardiovascular diseases - myocarditis, pericarditis, increased risk of stroke and diabetes.
The increased risk of stroke and diabetes is associated with periodontal disease, Dr. Sharkov also pointed out.
According to him, periodontal disease among pregnant women is a risk factor for giving birth to a low birth weight baby.
The risk of chronic kidney diseases increases from the complications of caries or due to periodontal disease, he added.
The program for the prevention of children's oral health began in 2010 with examinations of over 20,000 children and found that over 90 percent of them had at least one cavity, said Dr. Borislav Milanov, secretary of the state organization.
According to him, the program aims to cover children throughout the country, but there are areas where there are no children in the appropriate age group.
Sliven is the only area in which there is positive population growth, he also pointed out.
Dr. Milanov recalled that the program is for all children from 5 to 9 years of age, silanization is free, no certificates from institutions or referrals are required.
All that is required of the parent is to bring the child and give informed consent.
Within a year after silanization, children are followed up to check the condition of the sealants and, if necessary, make adjustments, he explained.
The difficulties before us are the small number of brochures dedicated to oral health and the possibility of silanization of teeth, as well as the sometimes difficulty of reaching parents, said Dr. Milanov.
About 500 dentists from all over the country are involved in the program, but the organization of work on the program needs to be improved, he added.
Untreated oral diseases affect half of the world's population, and in 30 years the incidence has increased by 1 billion people, Dr. Sharkov also pointed out.
The new National Program for the Prevention of Oral Diseases runs until 2026.
The incidence of caries in children has decreased by more than 40 percent
children
Dr. Nikolay Sharkov
a dentist
teeth
caries