How to recognize blepharitis, why it occurs and how to treat it, was told by
Volodymyr Melnyk, an ophthalmologist of the highest category, ophthalmic surgeon, candidate of medical sciences, medical director of the VISIOBUD clinic.
Causes of blepharitis
Blepharitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the edges of the eyelids of one or both eyes at the same time. It can be acute and chronic with periodic relapses. As a rule, later the acute form transforms into a chronic one.
Most often, the development of blepharitis is provoked by staphylococcal infection, which is present in the maxillary and frontal sinuses, tonsils, or on the skin. But it can also be done by the Demodex mite (Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis), which is localized in the eyelids, Haemophilus bacillus, herpes or chicken pox virus, intestinal bacteria. In this case, infectious blepharitis is diagnosed.
If it occurs against the background of diabetes, allergies, acute or chronic gastritis, cholecystitis, it is a non-infectious form of the disease.
The development of blepharitis can also be provoked by:
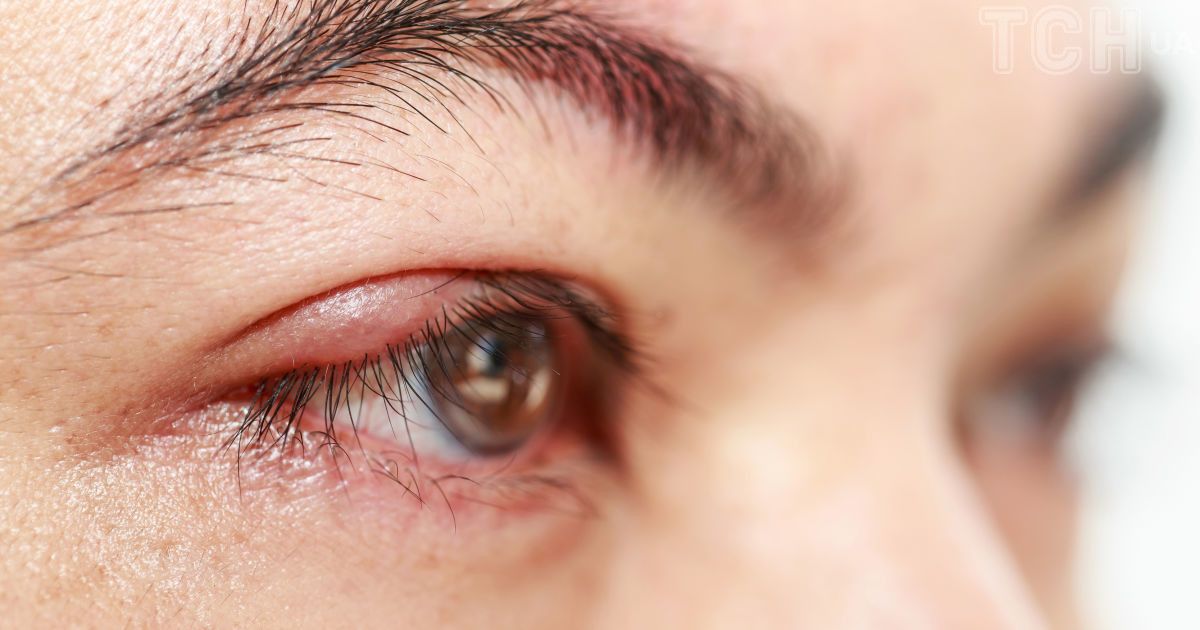
Symptoms of blepharitis
Manifestations of blepharitis depend, first of all, on the form of the disease, of which seven are distinguished - simple, seborrheic, staphylococcal (scaly), allergic, demodectic, acneic and mixed. And secondly, from the area of the affected eyelid:
1. front - inflammation affects only the edge of the eyelid with eyelashes;
2. posterior – the meibomian glands located deep within the eyelids are affected;
3. angular - inflammation is localized in the corners of the eyes.
For example, with a seborrheic form, white or yellowish scales accumulate on the front edge of the eyelids and at the roots of the eyelashes. These are skin cells (keratinocytes) and sebaceous glands (sebocytes) that cannot exfoliate normally.
For staphylococcal form - yellow crusts, which in the form of a so-called collar stick to the edge of the eyelids thanks to sebum. If they are peeled off, ulcers are formed, in place of which, after healing, scars are formed. Eyelashes can not only fall out, but also turn gray. And in the place of the formation of scars, later they do not grow, or they grow and fall out.
However, there are a number of symptoms that are observed in all forms of blepharitis. It:
Treatment of blepharitis and possible complications
In most cases, blepharitis is treated conservatively, that is, with the help of antiviral drugs, antibiotics, antihistamines, antiseptics in the form of drops and ointments. Hand hygiene and proper eye cleaning are a prerequisite for recovery. A complex of vitamins and trace elements that will help the visual system recover will not hurt.
However, the course of treatment is determined by an ophthalmologist individually during an eye examination, since it is very important to correctly determine the form of blepharitis. For this, special studies are carried out: eyelash microscopy, eye biomicroscopy, allergy tests, eye tissue histology, etc. If the patient has concomitant diseases such as diabetes, gastrointestinal disorders, anemia or any other, it is necessary to consult a family doctor and start therapy.
The main task of an ophthalmologist is to cure acute blepharitis in order to avoid the transition to a chronic form, which is characterized by periodic relapses. The return of the disease not only exhausts a person, but also causes the development of dry eye syndrome, keratitis, conjunctivitis, and acute meibolitis. In the absence of effective and timely treatment, the eyelid may turn outward or become scarred, in which case surgical intervention is performed.
Take care of yourself and your eyesight!